This article is to shade light on CMO/CRA/CMO or partnership selections and management, an extremely challenge aspect of the business. Based on my experience, the approach should be the same for development, research, or manufacturing. Of course, specific deliverables may vary, but the overall process remains consistent. For semantic purposes we will use CMO in the text to avoid redundance.
The first crucial step, is to clearly define what needs to be outsourced. Whether it’s research, full manufacturing, or development, precision and clarity are not just important, they are essential. During this phase, having a detailed document that outlines the requirements and timelines is not just extremely important, it’s a security blanket. Adhering to and agreeing upon project timelines is crucial, and it’s what will make us confident in our process.
From the initial idea of the product to be outsourced, we need to follow these steps:
“User” requirements
The CMO Selection and Approval Project Leader initiates and leads the compilation of the detailed description of the requirements for external manufacturing such as:
- Products in scope
- Country scope
- Regulatory scope
- Scope of outsourcing (manufacturing, packaging, …)
- Volume forecast
- Product and technical specifications
- Timeline requirements
- Business setup
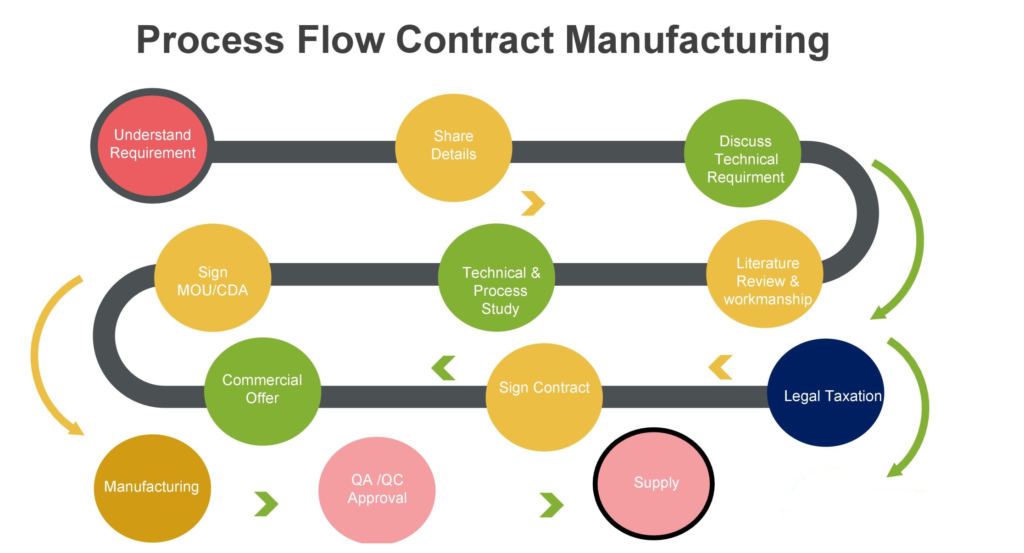
The following criteria’s are recommend in the screening process.
Service catalog
One of the first questions to be asked when selecting a CMO is whether it provides the range of services that you require.
Experience
One key consideration to choose a partner CMO is the verification of its experience. How many years has in the business for? Does it have expertise in specific therapeutic areas?
Geographical coverage
Territorial service coverage is extremely important when it comes to complying with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations. If you intend to manufacture or register a product in the European Union, you must adhere to EU GMP standards. Similarly, in the United States, you need to comply with USA GMP regulations, and the same applies to other regions. It’s crucial not to make the mistake of engaging a partner and then expecting them to obtain the necessary certifications.
Quality management
The importance of quality assurance cannot be overemphasized. Compliance and high-quality data is everything manufacture as this is the ground on which their drug development programs rest.
Reliable partners have quality management systems in place, in order to meet the principles of Good Clinical Practice (GCP), and international quality standards (e.g. ISO 9001, EU GMP, FDA).
How does your partners handle deviations? Are CAPA plans effectively managed? Is the CMO personnel well trained? Is the company certified? Sponsors should investigate these aspects before delegating their projects.
Responsiveness
Although it should not be the case, getting poor attention from vendors is sometimes a reality. Some suppliers show neither closeness nor responsiveness to their clients, and this might also happen with CMO. Sponsors should choose a CMO fully committed to their needs, a loyal team that pays full attention to their requests.
It may happen that larger CMO could prioritize bigger clients, while leaving aside smaller projects. In these cases, a small-size, more agile partner can be a better option.
Staff continuity
Many CMO have problems with staff retention, even with turnover levels above 20% for seven of the last ten years, according to a report.
Continuous personnel changes can negatively affect service quality and the relationships between the CMO and the sponsor’s team. On the other hand, long-term staff continuity improves and consolidates management processes.
Staff proficiency
The CMO workforce should not only show continuity but also technical proficiency. In order to guarantee technical ability, sponsors can audit the CMO internal training policies and records. In addition, detailed CVs of the CMO personnel assigned to the study should be reviewed to check employee education and expertise.
Technology
Pharmaceutical manufacturing involves multiple complex Technology plays a crucial role to ensure product efficiency and robustness. Meaning that you have a robust process that as been stressed and you can trust.
Financial stability
Pharmaceutical manufacture are large projects implying substantial investments and having to change a CMO in the middle of a transfer is a risk that causes technical and financial problems.
A CMO must be a trusted long-term partner not exposed to serious financial hurdles. Sponsors want to work with solid companies that ensure continuity of service.
Good questions to ask are the following: how many clients does the CMO have? How long has the company been operating for? Have revenues been increasing in recent years? Is the CMO experiencing growth? Sponsors are advised to check the financial health to verify the stability of such an important partner.
Pricing
Last but not least the CMO service rates should be evaluated. The price of service offerings may not be the most important factor when selecting a CMO, but still sponsors need to conduct their trials within budget. You should be well structured, and detailed on your budgets requesting a number of different financial proposals, and comparing then.
Once all information is available, the CMO selection team shall establish a decision matrix. Such decision matrix shall summarize and rank the suitability and capabilities of all partners in scope based on the categories of network strategy, quality, EHS, supply, security, IT, commercial and operational topics. Further aspects may be included with a documented justification if the projects require this.
Product flow, Financial Flow and contractual set-up
The setup of the supply and financial chain applicable to the project in scope needs to be documented in this step, providing information on the following topics:
- Contract Partners
- Contract types (Full service, partial service, License Agreement, Development Agreement, etc)
- Allocation of all production steps until release
- Financial/Tax considerations
- Product ownership
- Regulatory information
- Physical flow of materials / product(s)
- Flow of orders and forecasts
Supply Risk Assessment
Objective of the cross-functional Risk Management is to ensure a reliable market supply and timely availability of products from the selected contract manufacturer. In scope of the risk assessment are risks related to:
- Financial solidity of the potential manufacturer
- Risks due to geographical factors
- Risks due to geopolitical factors
- Considerations related to the need of a contingency for the supply
CMO QUALIFICATION INITIATION AND EXECUTION
In the CMO Qualification record, a Qualification Plan is set up to define the scope and the acceptance criteria for the CMO Qualification by compiling the sum of the requirements.
These tasks include but are not limited to:
- Receipt and assessment of the respective GMP Questionnaire
- Availability of information about the Manufacturing Site and related Authorizations (e.g. Manufacturing Authorization, GMP certificate, further certificates if applicable)
- GMP audit
CAPA FOLLOW UP
CAPAs which have been defined during the CMO qualification process shall be monitored by the respective Quality team during the CMO set up phase.
Once we have set up all the initial evaluation, we need to transfer the product, orders etc. However, since our purpose is not to discuss about transfers in the present text, we sill assume that the transfer is completes and in order.
CMO Management routine
This part of the Routine CMO management. In this part considered the second part of the life cycle management or the routine CMO Management.
In general most companies have an internal department in charge of managing the partners and those are reflected earther locally of globally, depending on the size of the company. This department can be Global, Regional, and Local, however in our experience a product or CMO team including several functions and in a cross- functional teams in more effective way for the governance and management, as well as establish the roles and responsibilities of each function. The specific structures for the partner management, such as territorial divisions, regional management groups, meeting frequency, or decision-making processes, will be tailored based on the needs of the relevant division, considering factors like the number of CMOs managed or the volume of products involved.
If you company does not have such department we advise to created. This department has several names but we will call GMT Global Management team. The objective of these team is to manage the day-to-day activities and directions to ensure business continuity through cross-functional alignment between CMOs and you. Some examples of activities for these team are:
- Forecasting, ordering, supply, risk management
- Inventory management / reconciliation
- Plan/development shipping requirements
- Import/export compliance
- Financial Flow (ordering, invoicing, tracking)
- Ongoing quality & compliance of CMOs with regulations and contractual obligations
- Establishment and maintenance of quality-related contractual agreements
- Execution and/or Quality oversight of a broad range of operational tasks
- Quality issue management and management of corrective / preventive actions (CAPA)
- Reporting and escalation of quality and compliance issues and risks
- Relationship management and communication with CMO quality experts
- Audits, quality performance and risk management of CMOs
PS: Most companies have one platform in which the supplier has access to it, similar to a common ERP but without the internal data it can be called Supply Network Collaboration Platform (SNCP).

CMO Performance Management
KPI monitoring
The performance of CMOs is monitored and reported routinely based on a defined set of key performance indicators (KPI).
Recommended KPI ‘s to be monitored
CSL = Customer service level
Are the CMO delivering what was proposed?
Conformance to the quality
Conformance to Quality KPI refers to a metric that measures the degree to which a product or service meets the specified quality standards1. It is a critical aspect of quality management, ensuring that the outputs consistently meet customer expectations and comply with regulatory requirements.
Destruction Level
Level of destruction of your product during the manufacture cycle. I recommend monitoring such KPI because if there are too many destructions due to process or logistics you can start to attack some of the problems. And expect the unexpected. Overall the critical part is to ensure the end to end supply of your product.
After all the analysis is recommended to have a yearly rating of the CMO. A mid-size pharmaceutical enterprise can have from 40 to 100 CMO’s which makes virtually impossible to manage all of them, therefore the KPI’s are critical parts of the management procedure.
Yearly CMO Rating
After the end of a calendar year a good approach is to rate your CMO The Supplier Evaluation process ensures that the performance of each individual CMO is properly assessed, documented, and improved.
The GMT can rate your CMO base of the different criteria chosen and the number of events that related. This rating number can be used not only for monitoring of the current number of CMO but also for future projects and new contracts. For large pharma companies this is one important number that dictates the relationship with the suppliers and future prospects.
The Supplier Evaluation process is vital to ensure that each individual CMO’s performance is adequately assessed, documented, and improved. GMT can effectively rate your CMO based on specific criteria and the number of rated events. This rating is essential for monitoring current CMOs and for future projects and contracts. It significantly impacts the relationships with suppliers and future prospects for large pharma companies. When dealing with multiple CMOs, priority should be given to those supplying the top products. It is crucial to focus efforts and resources on these key players to drive business outcomes. Key aspects include building and stabilizing relationships, analyzing conflicts, understanding perspectives, and driving win-win solutions with your partner. This demands transparent and supportive communication, regular visits, audits, and meetings. Avoid being blindsided by FDA warnings due to failed inspections. You must have a clear understanding of audit findings and anticipated closure dates. Ultimately, managing conflicts effectively is crucial; they are inevitable, but proactive and decisive approaches are essential.


Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?